Situatie
IdFix is used to perform discovery and remediation of identity objects and their attributes in an on-premises Active Directory environment in preparation for migration to Azure Active Directory. IdFix is intended for the Active Directory administrators responsible for directory synchronization with Azure Active Directory.
The Microsoft Office 365 IdFix tool allows you to identify and remediate object errors in the Active Directory in preparation for deployment to Azure Active Directory or Office 365. You can then successfully synchronize users, contacts, and groups from the on-premises Active Directory into Azure Active Directory.
Solutie
Install IdFix
1. Download IdFix
The setup will install the following prerequisites if they are not already present on your machine:
- Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5.2 (x86 and x64)
- Windows Installer 3.1
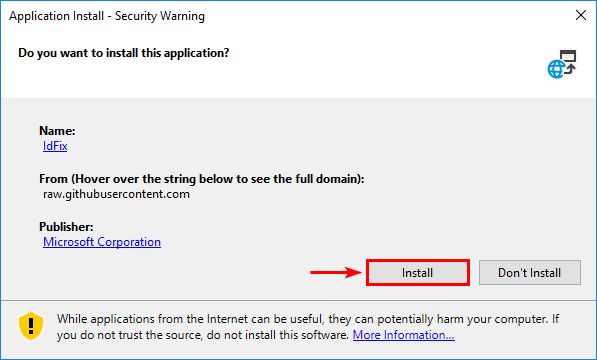
2. Run the setup.exe. It will ask you to install IdFix. Click Install.
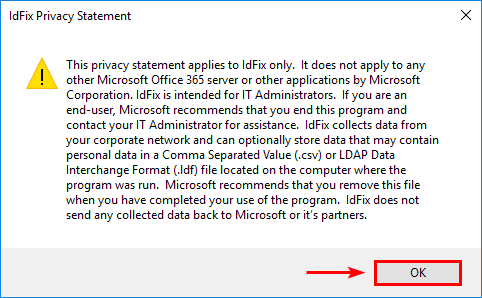
3. Accept the Privacy Statement. Click OK.
How to use IdFix
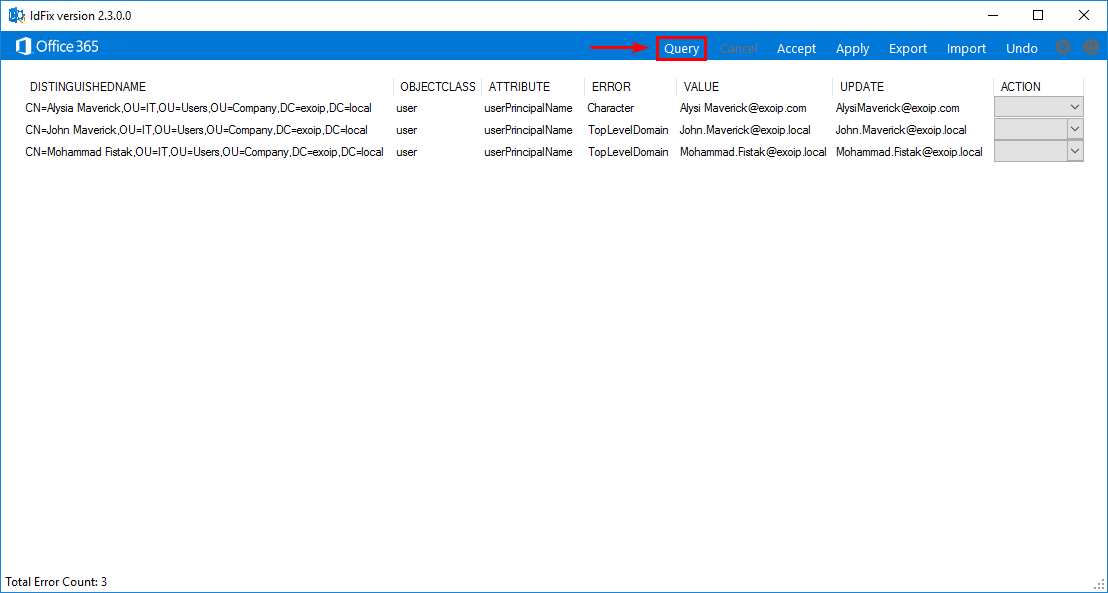
In IdFix, click on Query.
Note: You can get the Schema Warning message: The following attributes are present in the schema but are not marked for replication to the Global Catalog and will not be analyzed for errors. Ignore the message and click on Yes.
If there are errors, it will show the AD object with the error. Go to the AD object with the error and adjust the value.
In this example, there are three errors.
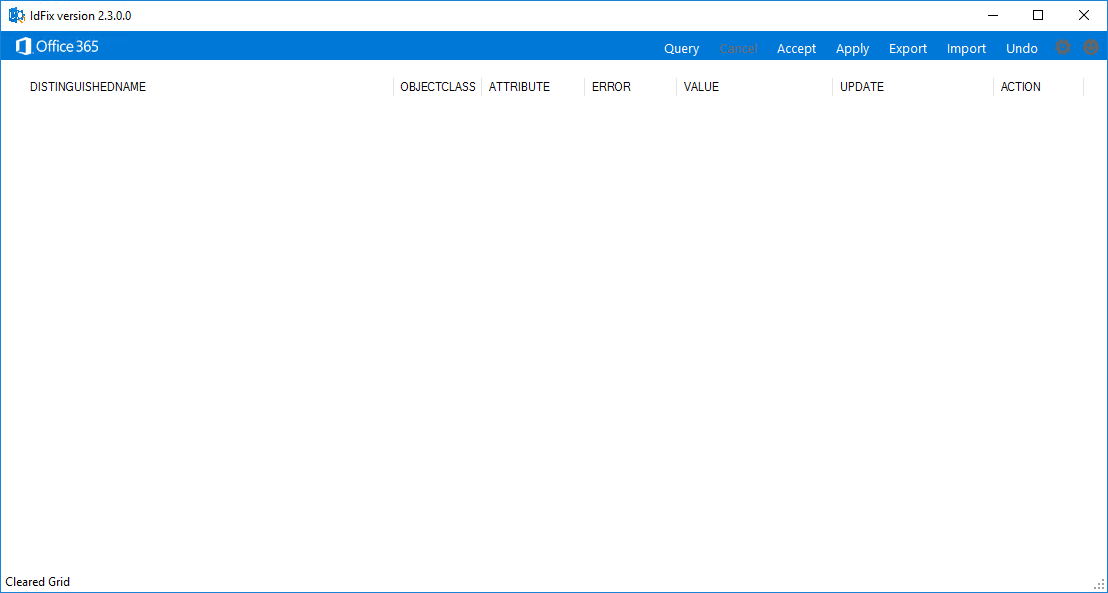
After fixing the errors, click on Query. Verify that list is empty.
IdFix errors
See the list of errors that you might see in IdFix.
| Error | Description |
|---|---|
| Character | The Value contains an invalid character. The suggested Update will show the value with the character removed. |
| Format | The Value violates the format requirements for the attribute usage. The suggested Update will show the Value with any invalid characters removed. If there are no invalid characters, the Update and Value will appear the same. It is up to the user to determine what they really want in the Update. For example, SMTP addresses must comply with RFC 2822, and mailNickName cannot start or end with a period. |
| TopLevelDomain | This applies to values subject to RFC 2822 formatting. If the top level domain is not internet routable, then this will be identified as an error. For example, an SMTP address ending in .local is not internet routable and would cause this error. |
| DomainPart | This applies to values subject to RFC 2822 formatting. If the domain portion of the value is invalid beyond the top level domain routing, this will be generated. |
| LocalPart | This applies to values subject to RFC 2822 formatting. If the local portion of the value is invalid, this will be generated. |
| Length | The Value violates the length limit for the attribute. This is most commonly encountered when the schema has been altered. The suggested Update will truncate the value to the attribute standard length. |
| Duplicate | The Value has a duplicate within the scope of the query. All duplicate values will be displayed as errors. The user can Edit or Remove values to eliminate duplication. |
| Blank | The Value violates the null restriction for attributes to be synchronized. Only a few values must contain a value. The suggested Update will leverage other attribute values in order to generate a likely substitute. |
| MailMatch | This applies to Dedicated only. The Value does not match the mail attribute. The suggested Update will be the mail attribute value prefixed by “SMTP:”. |
We did fix the synchronization errors on the AD objects with IdFix, and we are good to go. In the next step, we will install and configure Azure AD Connect.

Leave A Comment?