How to split a PDF File on Windows 11
The easiest built-in way to create a new PDF using chosen pages from an existing PDF is by using Microsoft Edge. Although this is a web browser, it allows you to view and work with PDF files.
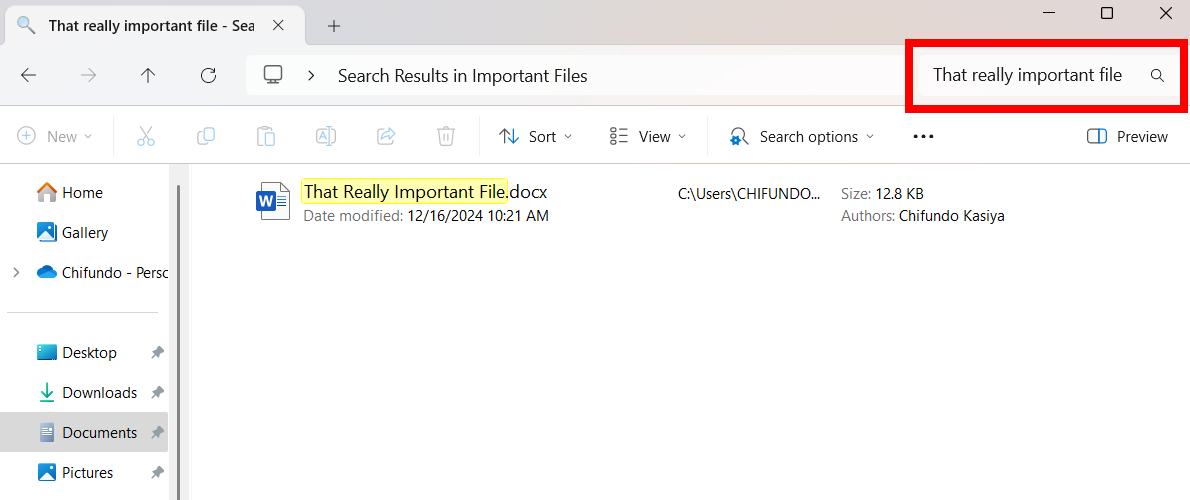
To start the process, launch File Explorer (press Windows+E) and find the PDF you want to split. Right-click the file and choose Open With > Microsoft Edge.
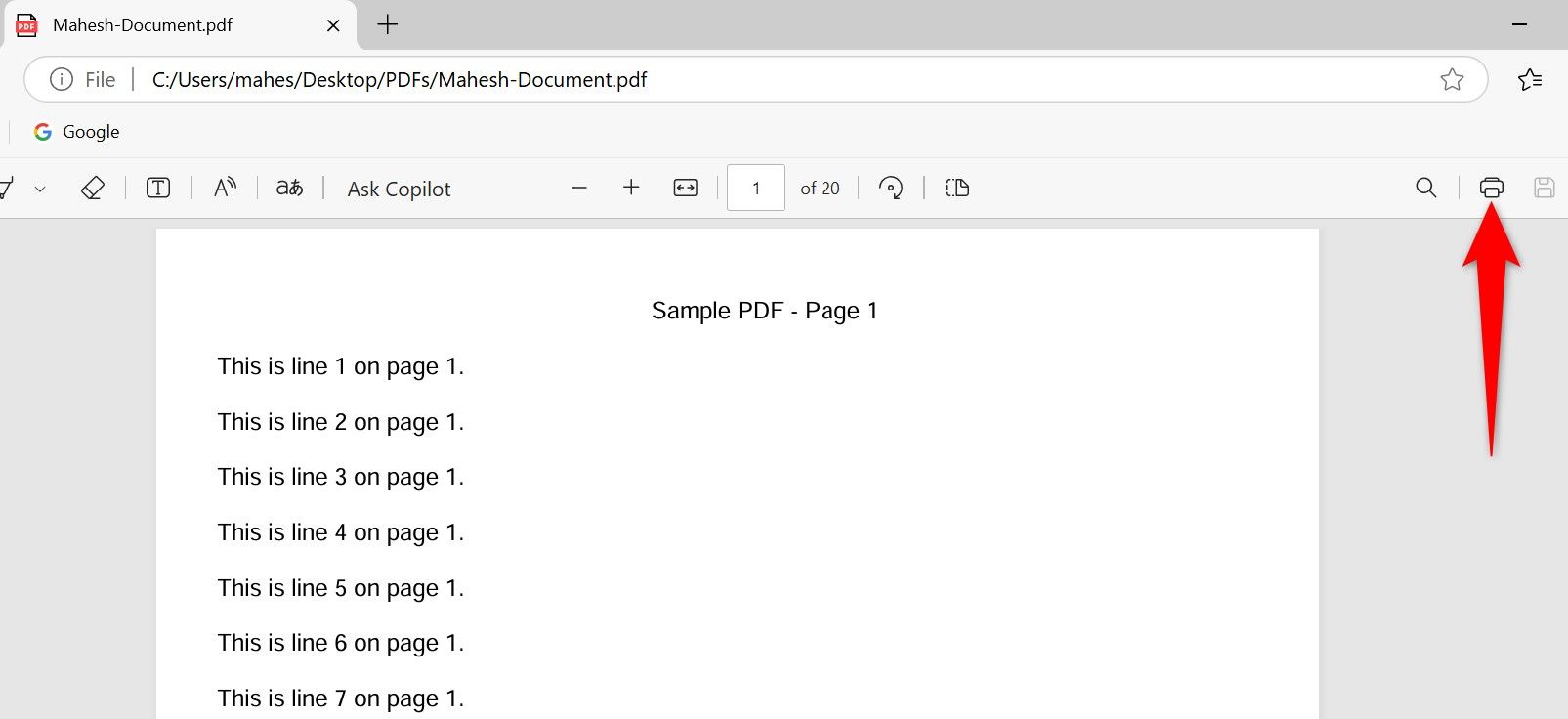
When the PDF is open in Edge, from the tool list at the top, click “Print” (the printer icon), or press Ctrl+P. Note that you aren’t actually printing anything.
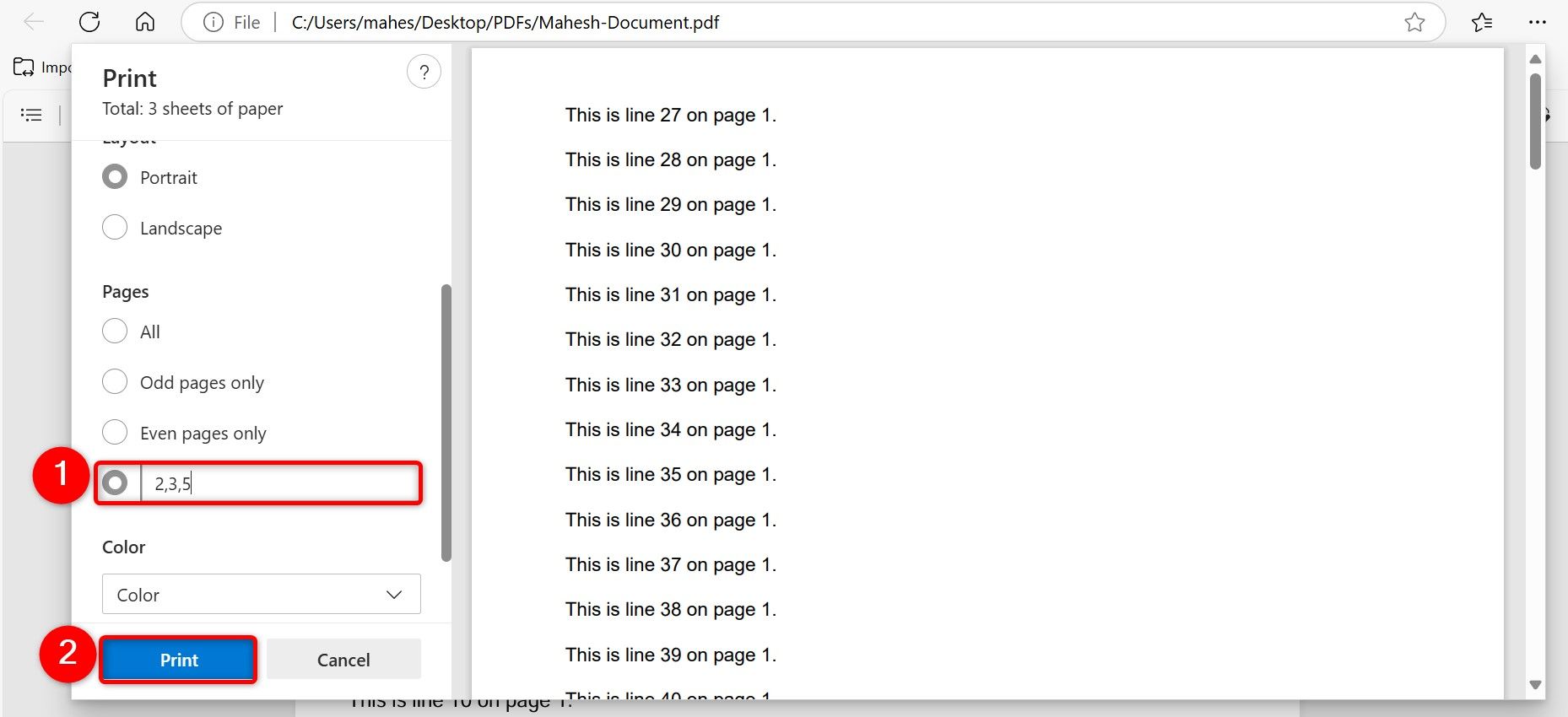
On the Print window, click the “Printer” drop-down menu and choose “Microsoft Print to PDF.” Scroll down and click the “Pages” field. Here, type the page numbers of the existing PDF you want in your new PDF. For example, to only extract the second page, type 2. To extract pages from 2 to 4, type, 2-4. To extract pages 2, 3, and 5, type 2,3,5. Then, at the bottom, click “Print”.
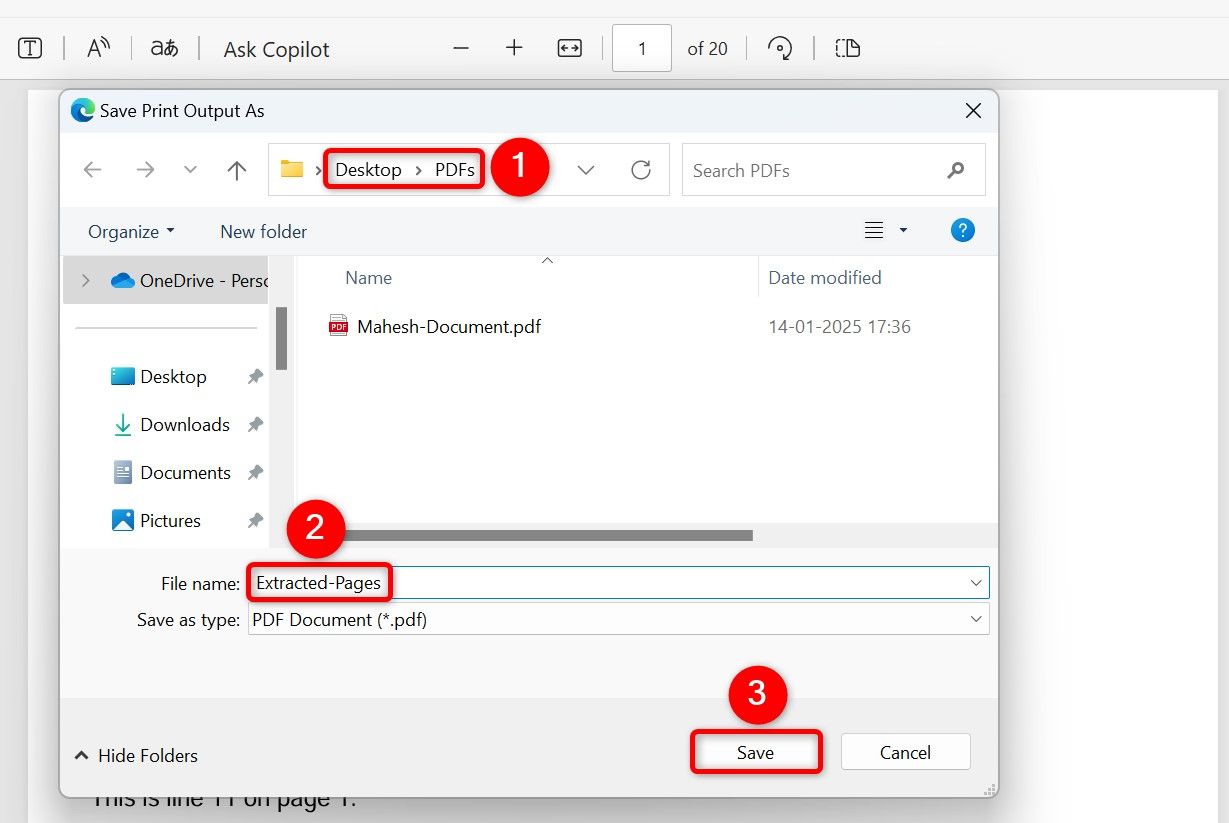
You’ll see the Save Print Output As window. Here, choose the folder to save your new PDF in. Select the “File Name” field and type a name for the file. Then, choose “Save”.
Make a New PDF From Chosen Pages Using a Free App
Another way to split a PDF is by using a free app called PDF Merger & Splitter. To use it, launch Microsoft Store on your PC, type PDF Merger & Splitter in the search box, press Enter, select the app in the search results, and choose “Get”.
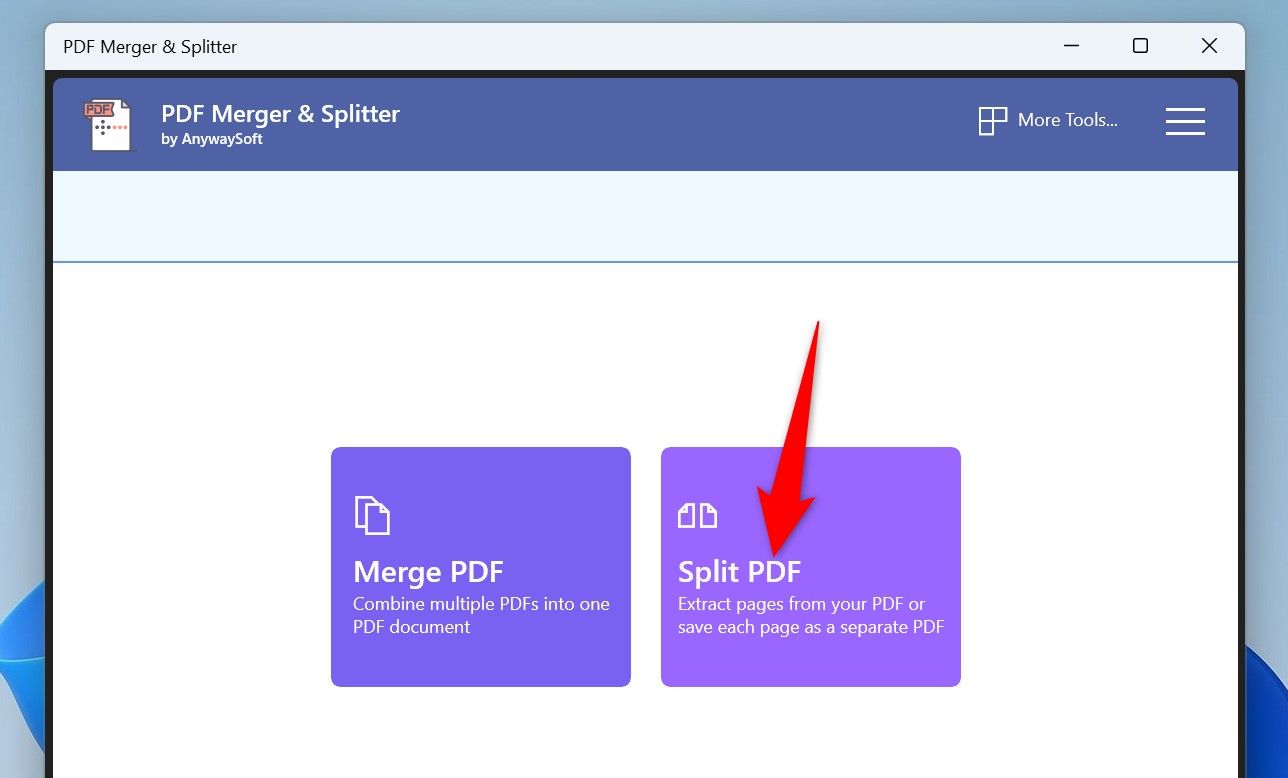
Open the newly installed app and choose “Split PDF”.
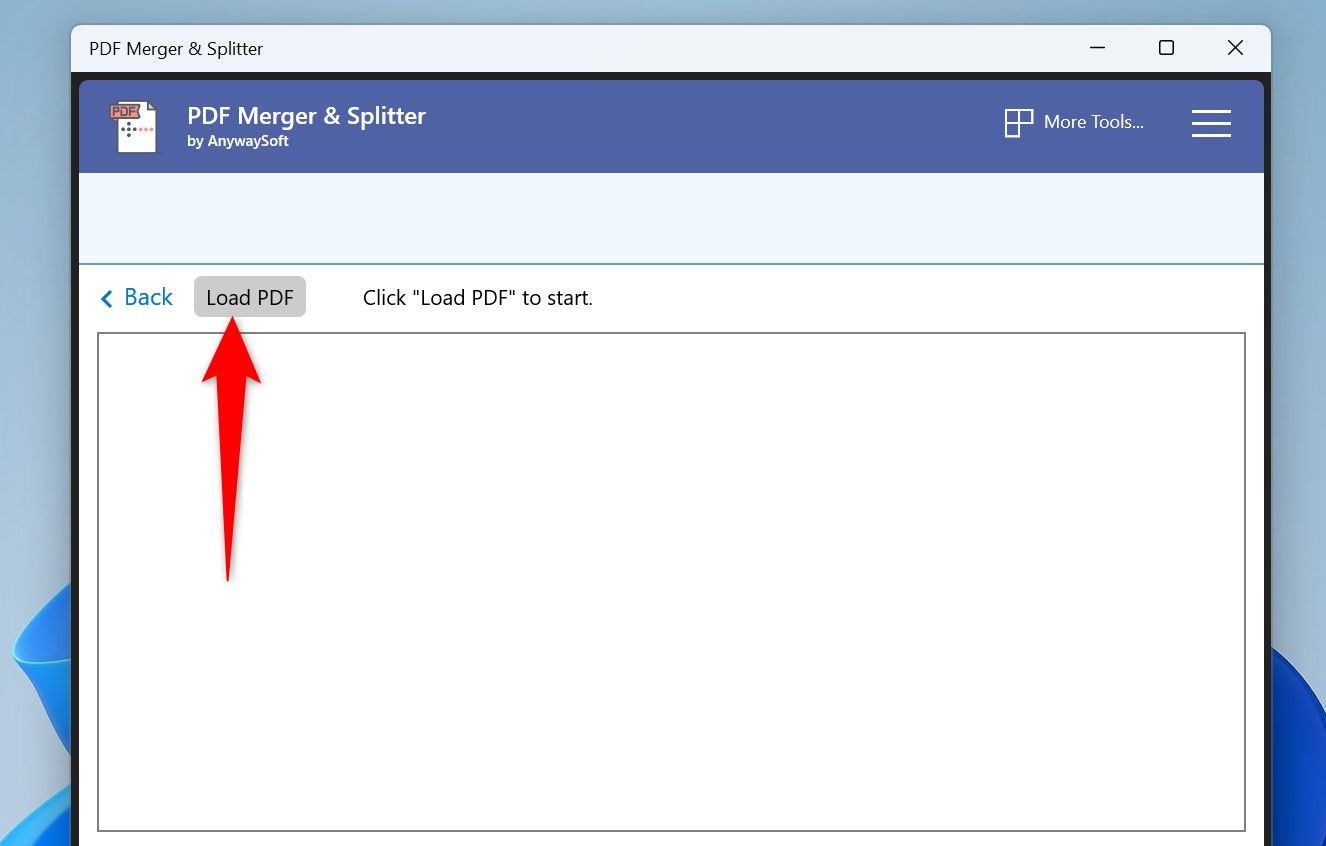
Click “Load PDF” at the top and select the PDF you want to split.
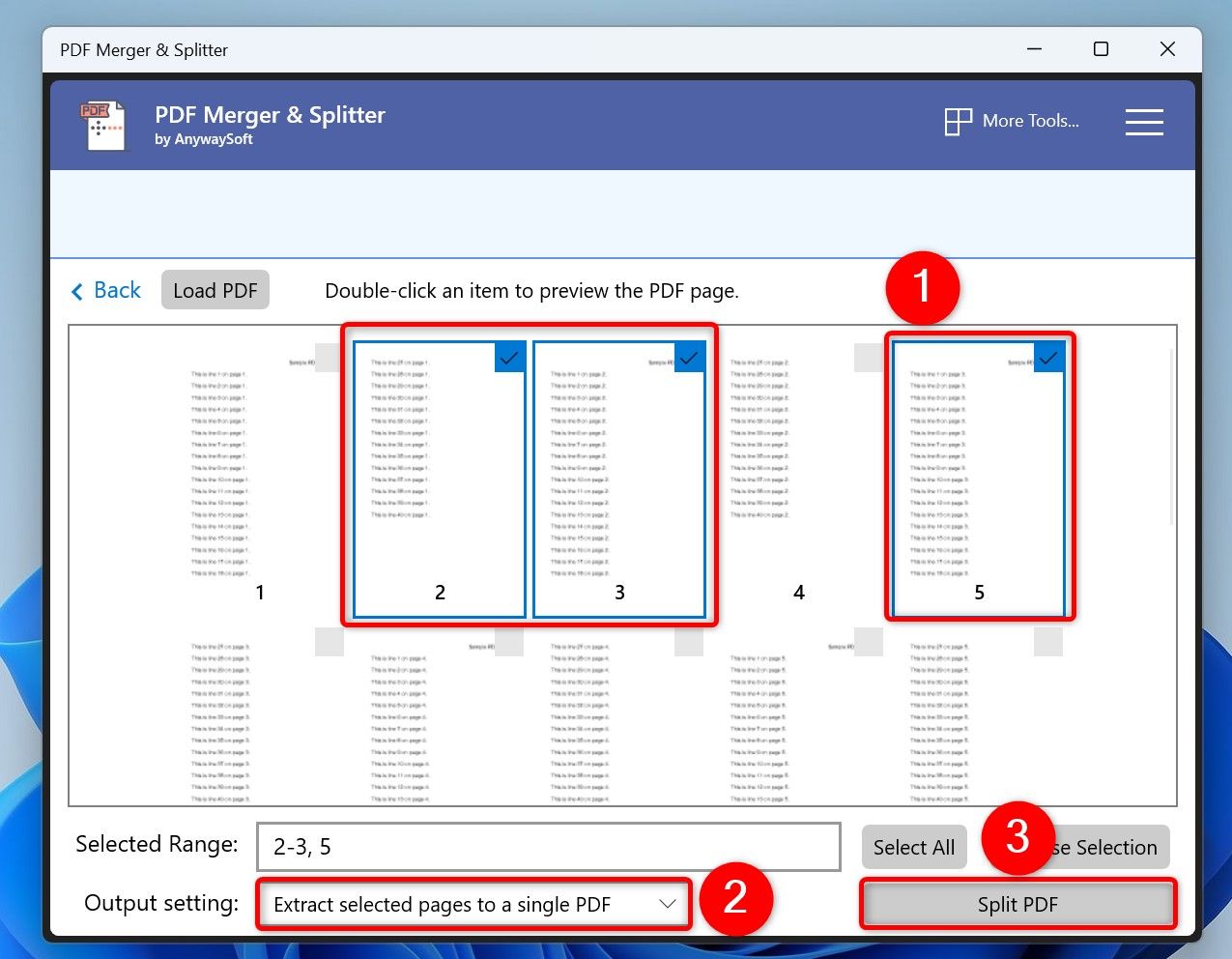
When the PDF is loaded, you’ll see each page’s preview. Click the pages you want to create a new PDF from. As you select pages, the app fills in the page numbers in the Selected Range field.
- Extract Selected Pages to a Single PDF: This option extracts the selected pages from the loaded PDF file and makes a single new PDF.
- Extract Each Selected Page to a PDF: This option turns each selected page in the source PDF file into a new PDF file. You’ll have one PDF for each page.
Then, click the “Split PDF” button at the bottom.
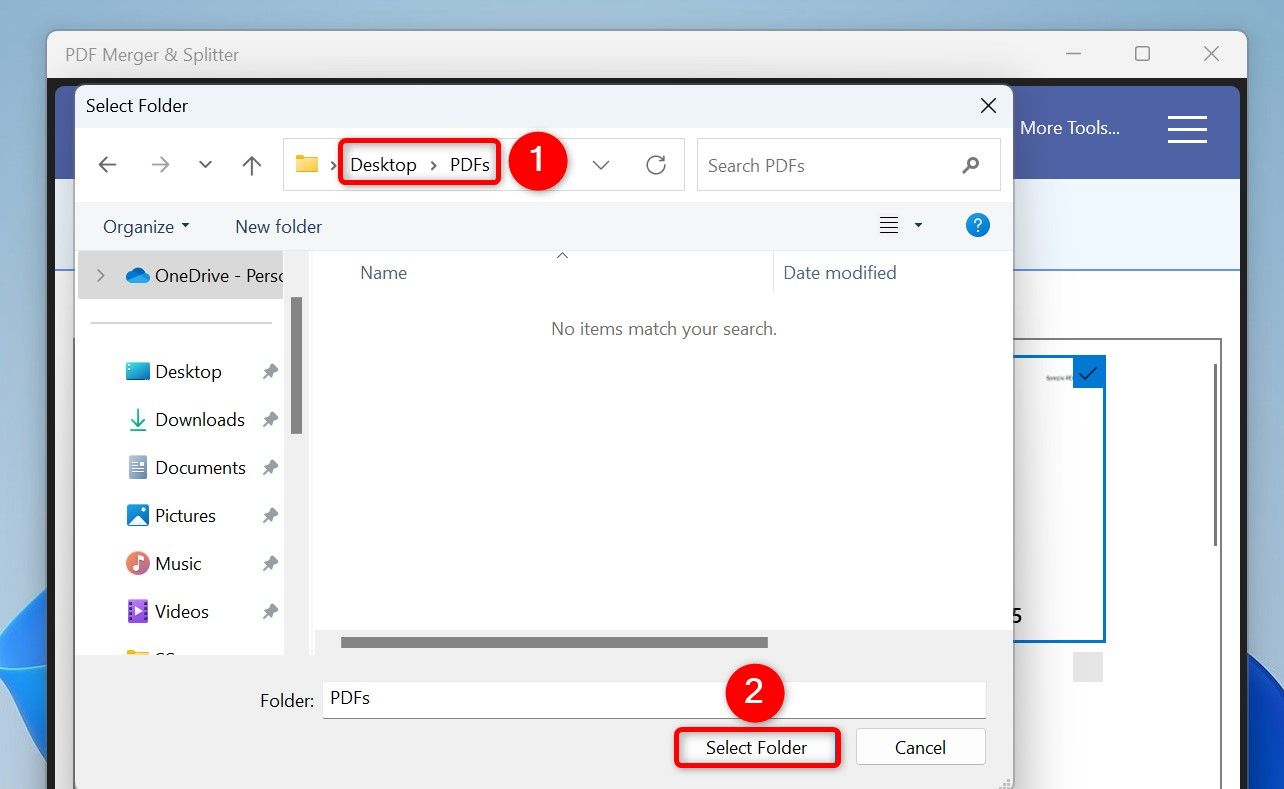
Choose the folder in which you want to save the resulting PDF and click “Select Folder”.
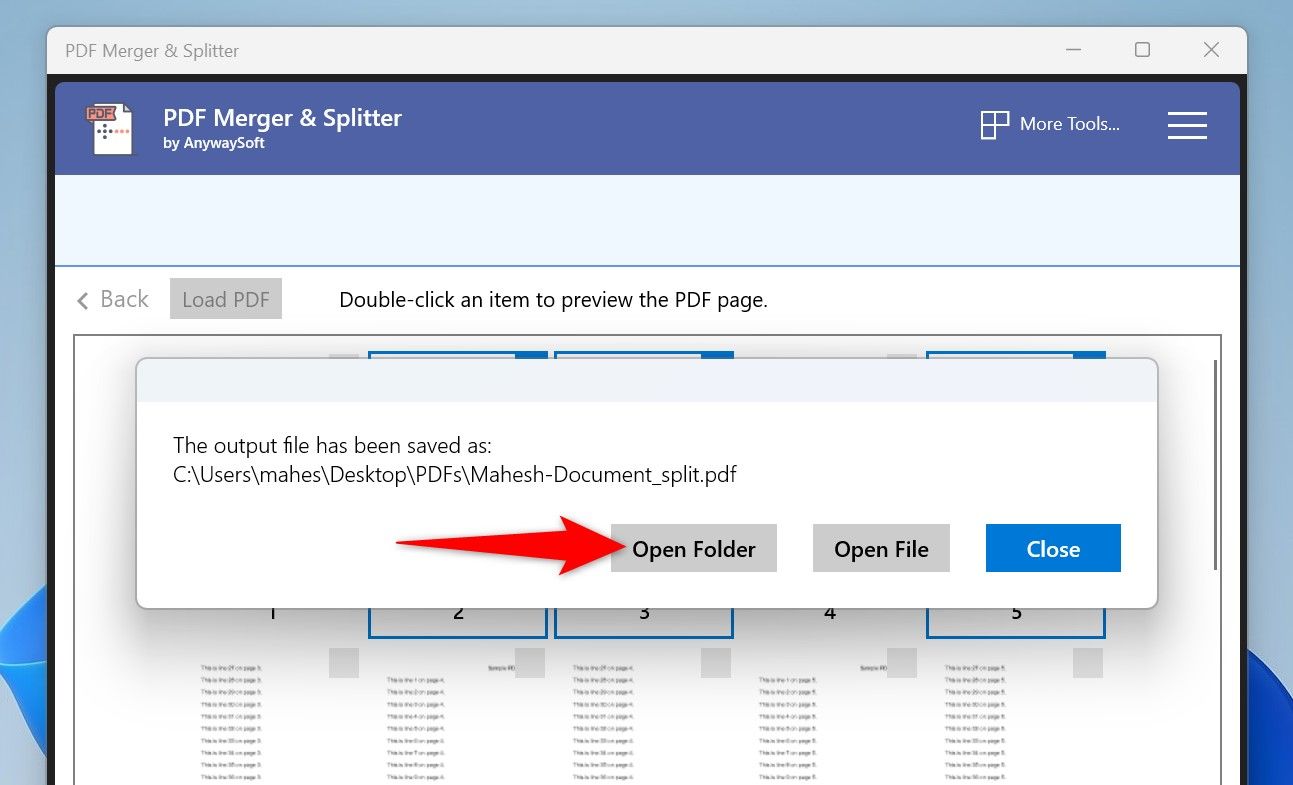
In the open prompt, click “Open Folder” to open the folder where your split PDF is located.
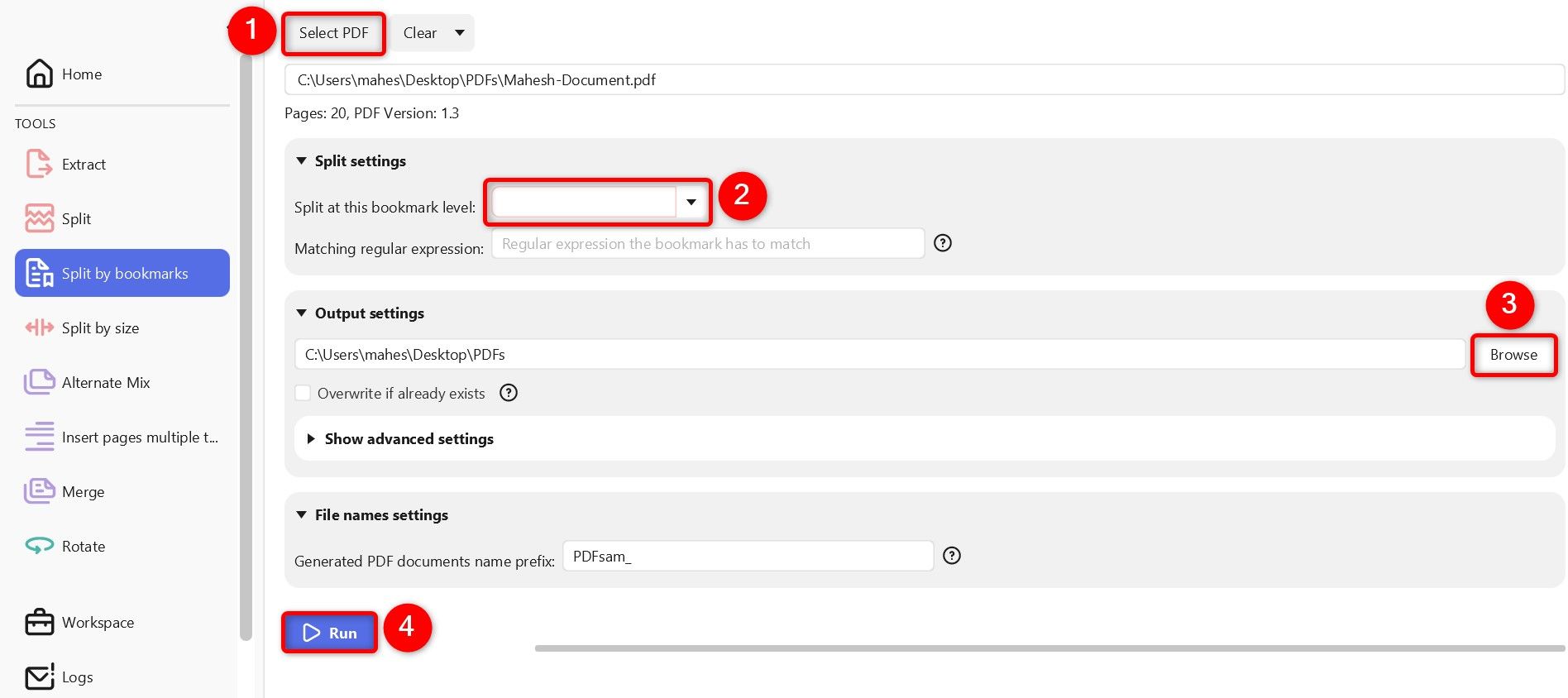
If you’re looking for more advanced options, like the ability to split a PDF by every n number of pages, after the specified page numbers, or bookmarks, use the free and open-source PDFsam Basic app.
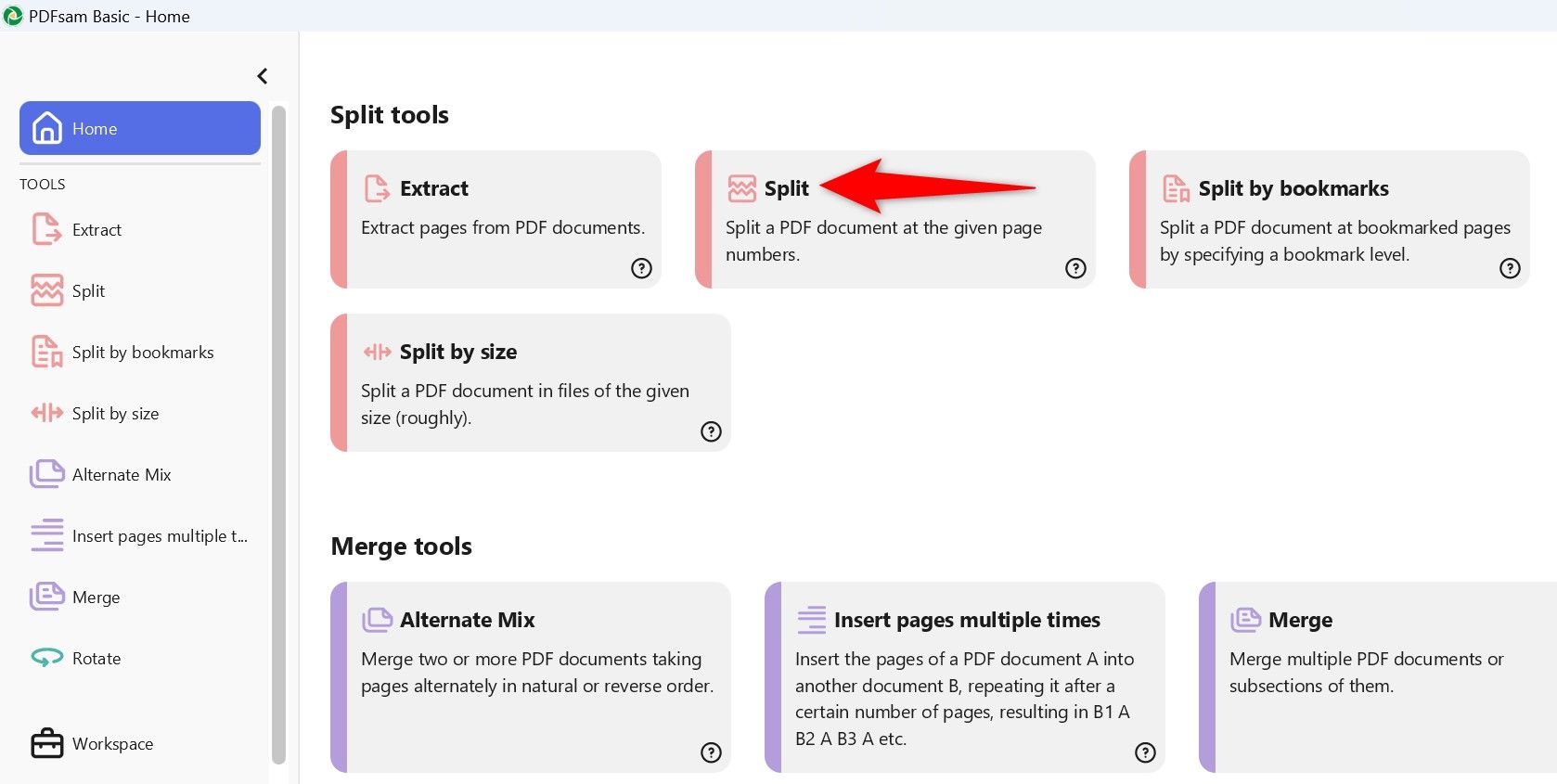
Launch the newly installed app. In the Split Tools section, click “Split”.
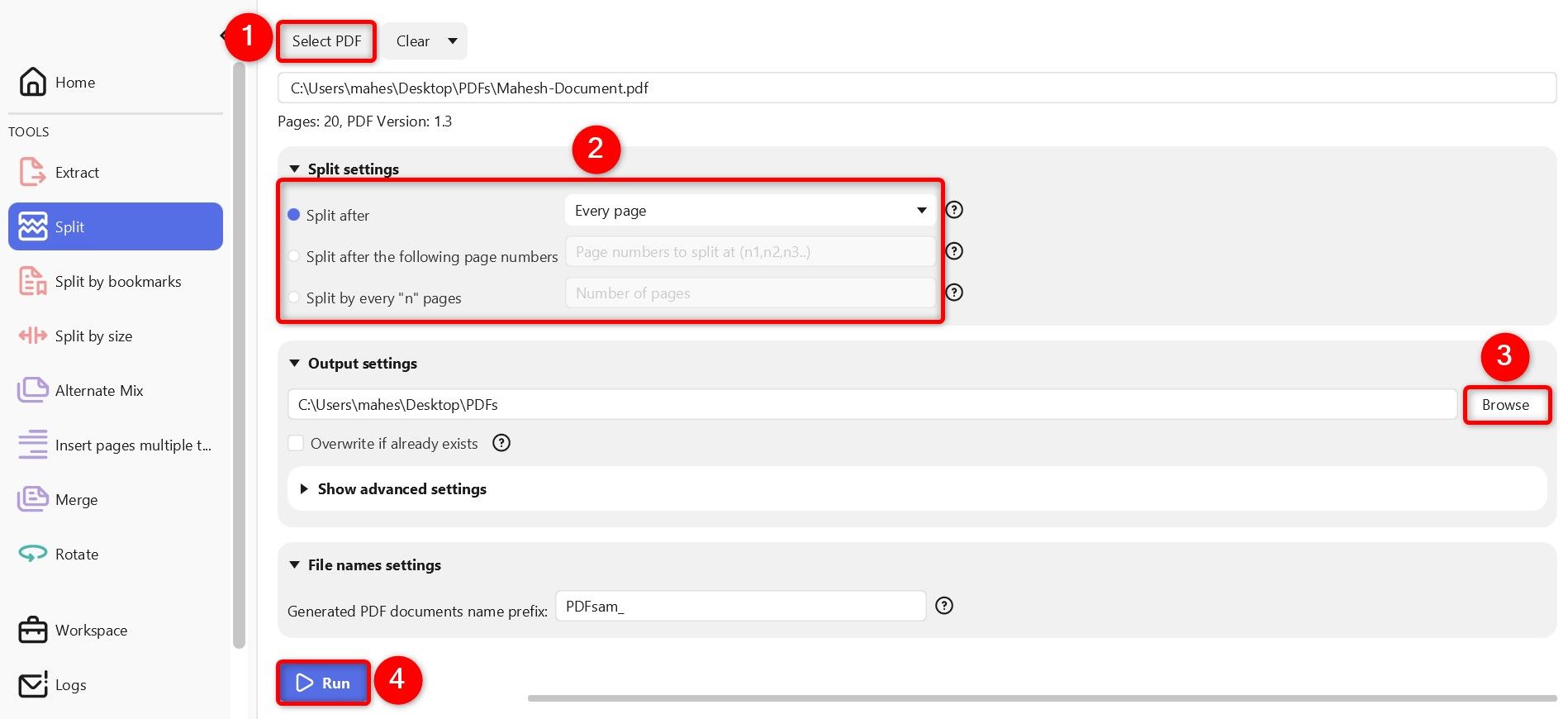
At the top, click “Select PDF” and choose the PDF you want to split. In the Split Settings section, select how you want to extract pages from your file:
- Split After: This option splits your PDF after Every Page, after Even Pages, or after Odd Pages.
- Split After the Following Page Numbers: This option splits the PDF after the specified page numbers.
- Split by Every N Pages: You specify the N number and the app splits the PDF for every N page.
In the Output Settings section, click “Browse” and choose where you want to save the resulting PDF files. Then, at the bottom, click “Run”.
If you only have one or a few PDFs to split, you can use a web-based app to perform the task. This eliminates the need to download and install an app. Some tools you can use are Adobe Acrobat and iLovePDF. Note that I don’t recommend using this method for confidential files, as you risk exposing your file’s data to these web-based services.
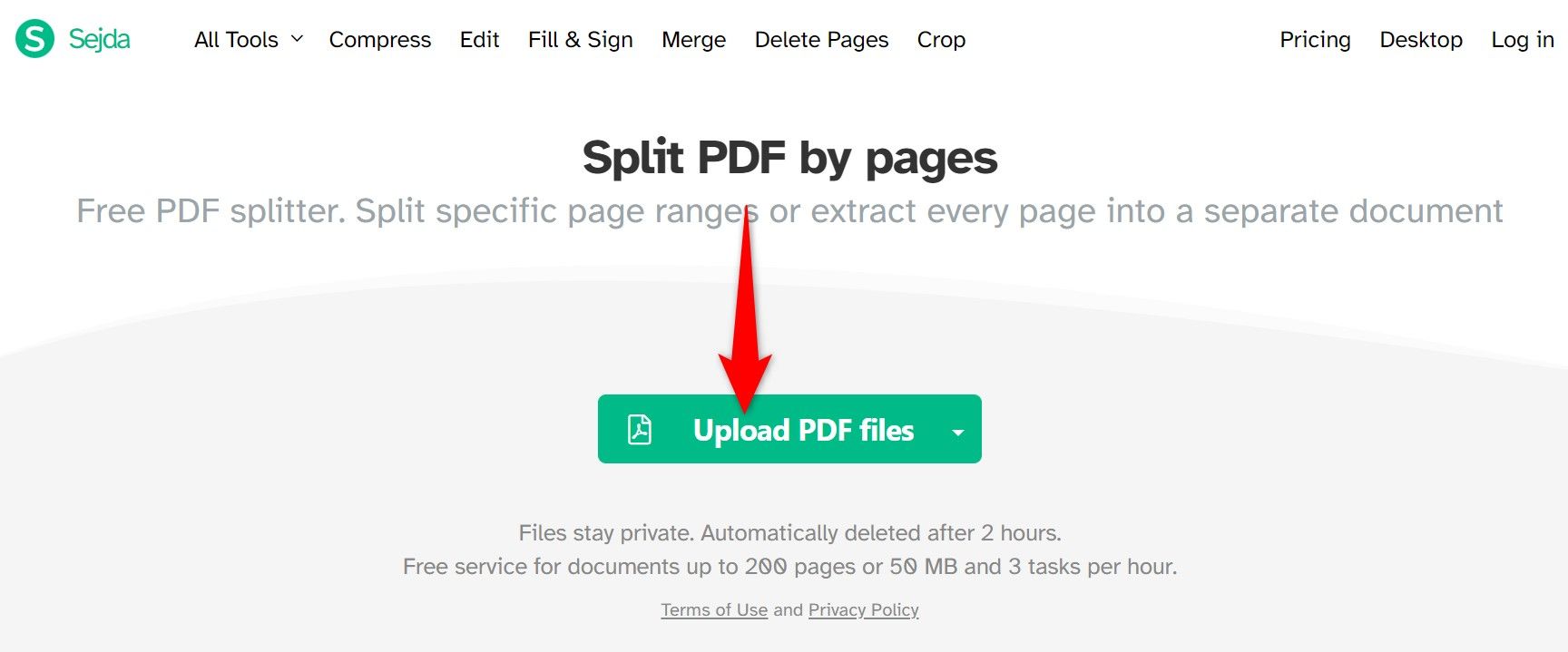
To use the Sejda method, launch its site, click “Upload PDF Files,” choose your PDF, and wait for the file to upload.
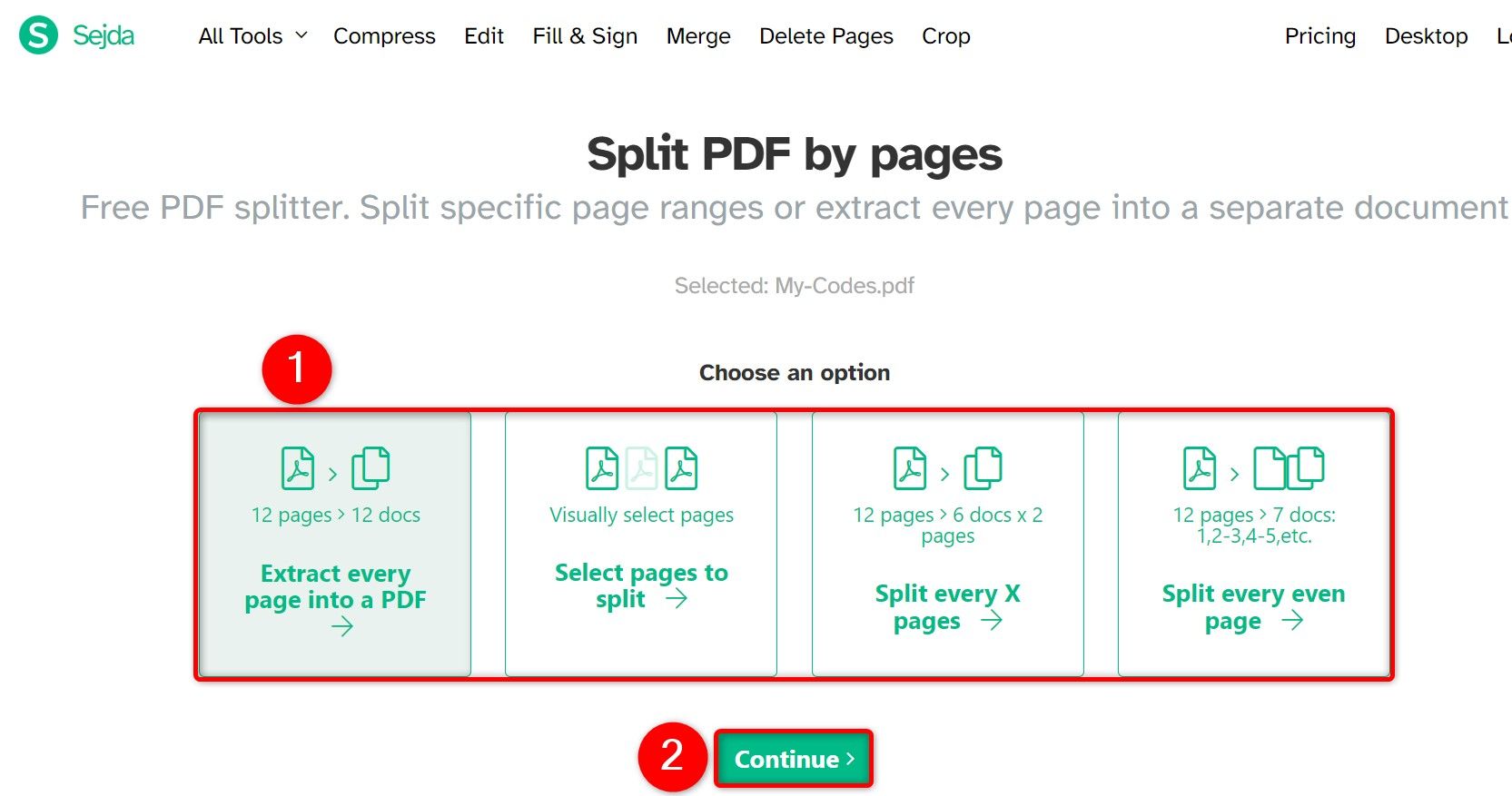
Choose how you’d like to split the file. Your options are:
- Extract Every Page Into a PDF: This turns every page in your PDF into a new PDF file.
- Select Pages to Split: This allows you to select the pages in your PDF to then turn into a new PDF file.
- Split Every X Pages: This option lets you create a new PDF after every X number of pages.
- Split Every Even Page: This option splits the PDF after every even page.
I’ll choose the “Select Pages to Split” option. Then, choose “Continue”
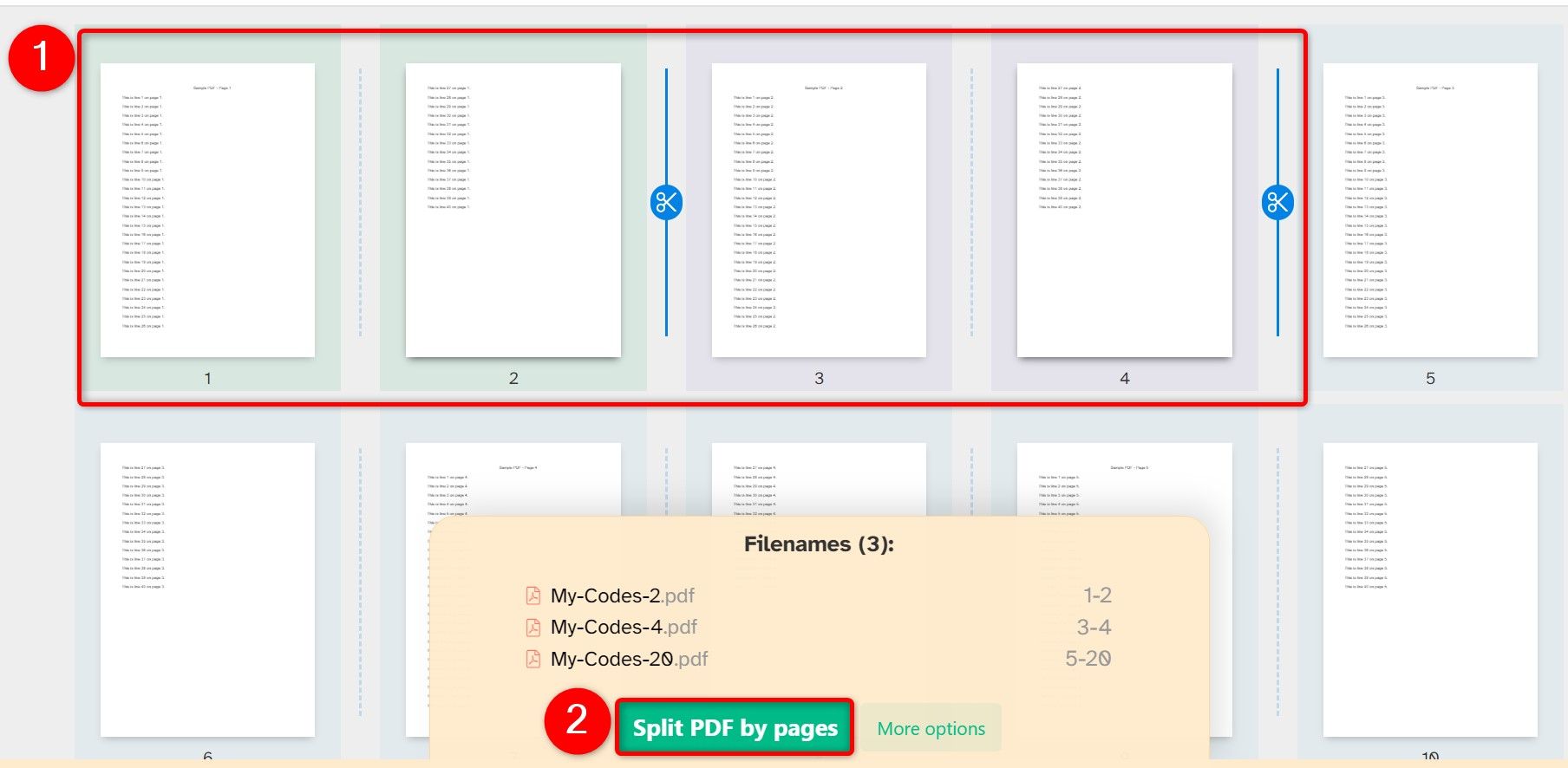
On the following screen, select the pages to extract. Click the dividing line, and the pages to the right of the line will go into a new PDF. When you’ve made your selection, at the bottom, click “Split PDF by Pages.”
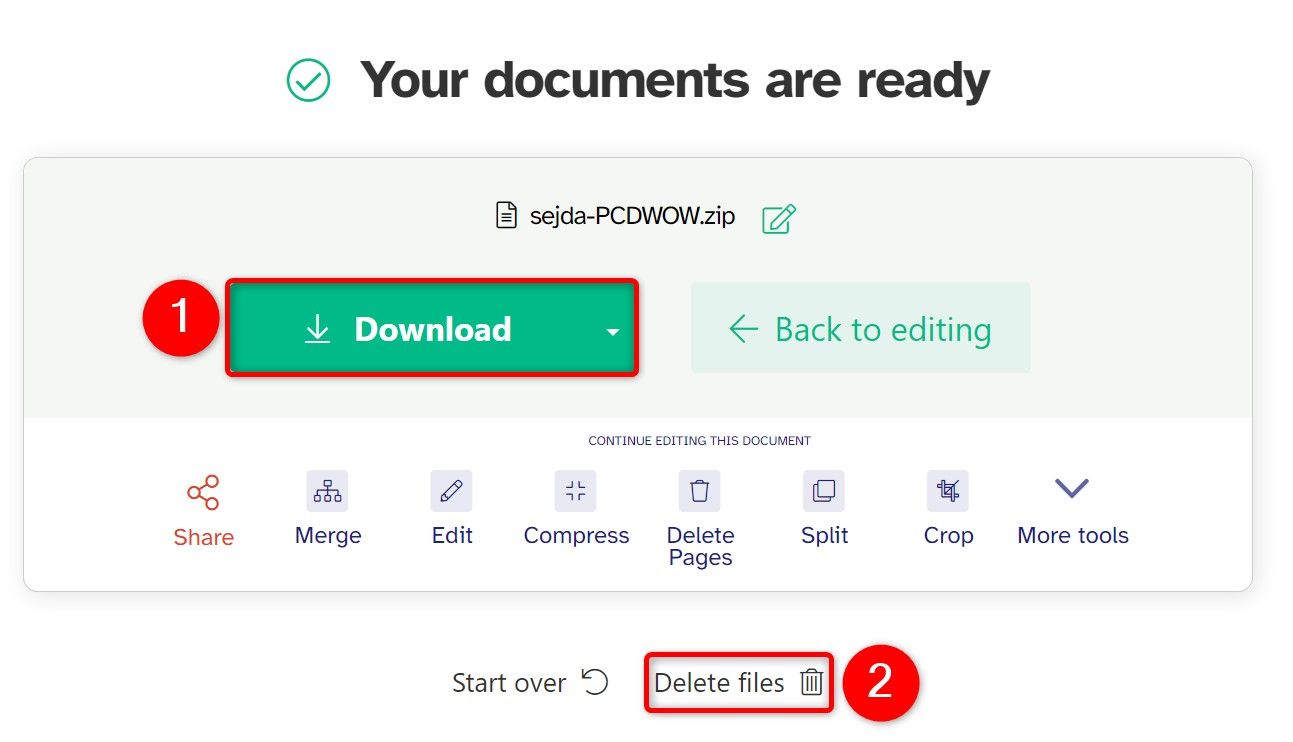
Select “Download” to save the resulting PDF(s) to your PC. Then, click “Delete Files” to remove your PDF from the site’s servers.