Situatie
How to use the Azure CLI to deploy a Linux virtual machine (VM) in Azure.
The Azure CLI is used to create and manage Azure resources from the command line or in scripts.
We will be installing Ubuntu 16.04 LTS
Solutie
Launch Azure Cloud Shell
Create a resource group
Create a resource group with the az group create command. An Azure resource group is a logical container into which Azure resources are deployed and managed. The following example creates a resource group named myResourceGroup in the eastuslocation:
Create virtual machine
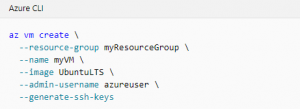
Create a VM with the az vm create command.
The following example creates a VM named myVM and adds a user account named azureuser. The --generate-ssh-keys parameter us used to automatically generate an SSH key, and put it in the default key location (~/.ssh). To use a specific set of keys instead, use the --ssh-key-value option.
It takes a few minutes to create the VM and supporting resources. The following example output shows the VM create operation was successful.
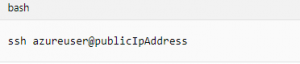
Note your own publicIpAddress in the output from your VM. This address is used to access the VM in the next steps.
Open port 80 for web traffic
By default, only SSH connections are opened when you create a Linux VM in Azure. Use az vm open-port to open TCP port 80 for use with the NGINX web server:
Connect to virtual machine
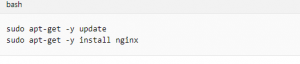
Install web server
To see your VM in action, install the NGINX web server. Update your package sources and then install the latest NGINX package.
When done, type exit to leave the SSH session.
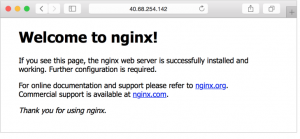
View the web server in action
Use a web browser of your choice to view the default NGINX welcome page. Use the public IP address of your VM as the web address. The following example shows the default NGINX web site:
Clean up resources
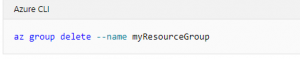
When no longer needed, you can use the az group delete command to remove the resource group, VM, and all related resources.


Leave A Comment?